HANA.EXPERT Healthcare Cloud Protection for Salesforce.com is the only security solution on the market designed to prevent attacks via files and URLs uploaded to Salesforce.com.
Cloud ecosystems operate on a shared security responsibility model. Salesforce.com does a great job of covering various aspects of system and application level security. However, it is Salesforce.com subscribers' responsibility to secure files and links uploaded to Salesforce.com platforms by their customers and employees.
It's an essential component of your overall security strategy, and thanks to its Cloud-to-Cloud architecture, requires no middleware. As progressively more organizations outsource more of their IT infrastructure to the cloud, the duties of security personnel have changed, but not vanished — which is confirmed by the proliferation of ransomware and malware threats to cloud-based services.
However, customer security responsibilities differ across the spectrum of cloud-based service models. This variation in liabilities and duties between clients and providers requires that security professionals have a strong understanding of the Shared Responsibility Model.
This means understanding the general trends in Shared Responsibility Models across types of services as well as the individual details of shared responsibilities within the context of each specific service. In general, as the extent of outsourcing to the cloud increases, the security responsibilities of providers grow. Nevertheless, customers of cloud-service providers are always responsible for the content and data on the cloud as well as the user endpoints that access the cloud. For this reason, it is important to consider cloud-based security solutions that complement the security features offered by cloud service providers, with preference given to security solutions that work natively within the cloud.
There are many factors to be aware of when reviewing cloud-based services, but there are at least three key directives that should always be followed: (1) include the cloud in your business and security strategy, (2) understand your responsibility, and (3) choose your vendor carefully. Despite the changing landscape of threats and vulnerabilities, security personnel must not forget the basics of cyber security — the latest cloud innovations will never change sound fundamentals.
CISOs and security leaders must understand the scope of their responsibilities for security in the cloud. Provider-supplied security differs among infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS) models.
- Regardless of the model, data security as well as identity and access management (IAM) remain customer responsibilities.
- The cloud reduces the scope of required traditional security work, but cannot eliminate it. Moving processes to the cloud does not automatically make them "more secure".
- Establish a security control plan using third-party tools to achieve better visibility, data security, threat protection, and compliance — preference should be given to third-party tools that are integrated directly into the cloud platform without middleware.
- Fully leverage provider-supplied security measures, and avoid solutions that interfere with, bypass, or reduce provider-supplied security measures.
- The Shared Responsibility Model of course applies to compliance just as it does to security, so make sure you understand the compliance requirements of all aspects.
- Do not settle for cloud partners or third-party solution providers that cannot demonstrate proven security levels through tests conducted by independent firms (e.g., AV-Test and AV-Comparatives).
- Most traditional security best practices still apply to public cloud systems, such as defense in depth and the necessities of next-gen anti-malware, security controls, logging, reporting, and alerts.
Shared Responsibility Model
- The customer is both accountable and responsible for all aspects of securing and operating solutions when they are deployed on-premises.
- With IaaS deployments, elements such as buildings, servers, networking hardware, and the hypervisor, should be managed by the platform vendor. The customer is responsible or has a shared responsibility for securing and managing the operating system, network configuration, applications, identity, clients, and data.
- PaaS solutions build on IaaS deployments, and the provider is therefore additionally responsible for managing and securing the network controls. The customer is still responsible or has a shared responsibility for securing and managing applications, identity, clients, and data.
- With SaaS systems, a vendor provides the application and abstracts customers from the underlying components. Nonetheless, the customer continues to be accountable, must ensure that data is secure and free of malware, and shares the responsibility of managing their users and endpoint devices.
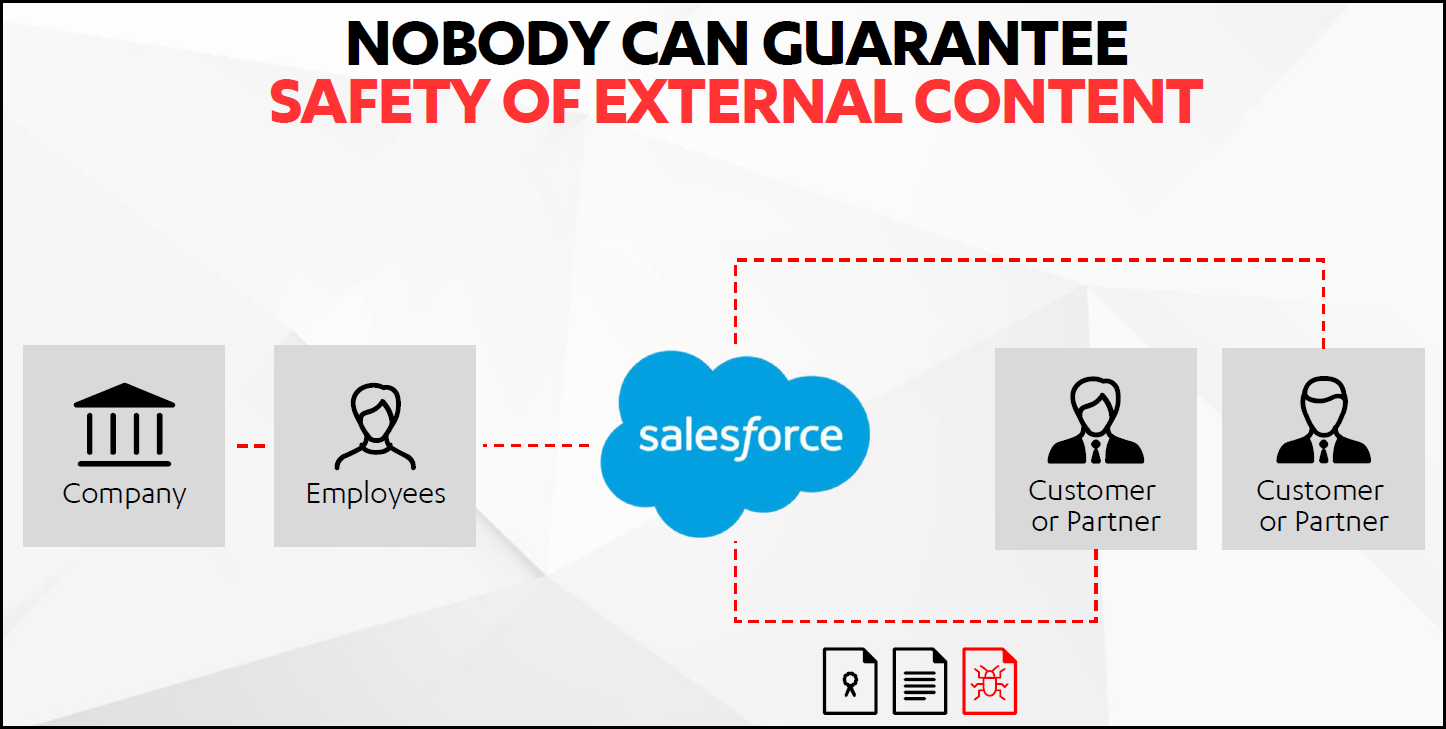
Modern ways of working have demanded collaboration and data sharing approaches that heavily utilize cloud-based services. Unfortunately, as individuals share data through cloud applications, they risk the spread of malware designed to infect these systems. As noted previously, the systems of 11% of organizations have explicitly sanctioned cloud apps infected with malware.
As many organizations provide direct access for cloud applications through their firewalls and other network security functions, protection against malware, ransomware, and malicious links is often left solely to endpoints. This makes systems more vulnerable to attacks and boosts the likelihood of successful attacks — and this exposure becomes worse as the number of complementary security layers decreases.
Furthermore, in instances like the Cerberus attack targeting an Office 365 vulnerability, the chance of spreading the malware to other parts of the organization increases significantly — notably in use cases such as intranets, customer and partner communities, or any other cloud platform that allows sharing of files or links.
Layered Security with Salesforce Cloud Protection

Safety of External Content for Salesforce Cloud
For more information, please contact:
Sales at 302 715-0062 or This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.